Reasons for filter integrity test failure
2025-06-09 Eternalwater In pharmaceutical production, sterilizing filter integrity testing is the core link to ensure sterility and safety. This article will focus on the key issue of integrity test failure, analyze the various reasons that lead to test failure, and explore the corresponding response decisions to ensure the safety and quality of pharmaceutical production.
If the sterilizing filter fails the integrity test, it may be damaged, but there are other possible reasons for failure, including instrument problems, pipeline tightness, human operation (such as incorrect assembly, wrong parameter setting, etc.) and incomplete wetting, etc. The filter failure investigation and retesting procedures should be recorded.
Analysis of test failures caused by insufficient wetting
Insufficient wetting may be caused by insufficient rinsing of the filter, which does not wet all the pores. If the test is performed after use, it may also be caused by the adsorption of hydrophobic contaminants by the filter, or other formulation components that change the surface wetting properties of the filter membrane. Changes in wetting properties may affect the integrity test performance. For example, pipe material may enter the product flow and be adsorbed by the filter membrane, or product residues may not be cleaned up, affecting the wetting properties of the membrane, resulting in integrity test failure.
In order to obtain appropriate integrity test results, the porous structure of the filter should be completely wetted, as the physical nature of the integrity test method relies on the flow of gas through a wetting liquid layer. The wetting of the filter membrane can be affected by the following factors:
1.Membrane polymers: Some polymers are more wetted than others, depending on the critical surface tension of the membrane material.
2.Pore size: The smaller the pores, the harder it is to wet.
3.Wetting Fluids: Certain wetting fluids may have repulsive interactions with the polymer matrix.
4.Product residues or contaminants: Product residues or contaminants can change the hydrophilicity of the membrane polymer, repelling wetting fluids or reducing surface attraction.
5.Pressure conditions: The manufacturer's pressure recommendations should be followed to achieve complete wetting of the membrane.
6.Temperature conditions: Temperature affects the surface tension of the wetting fluid.
In addition to the above, there may be process or application related factors that affect the integrity test and are not covered by the manufacturer's instructions for use.
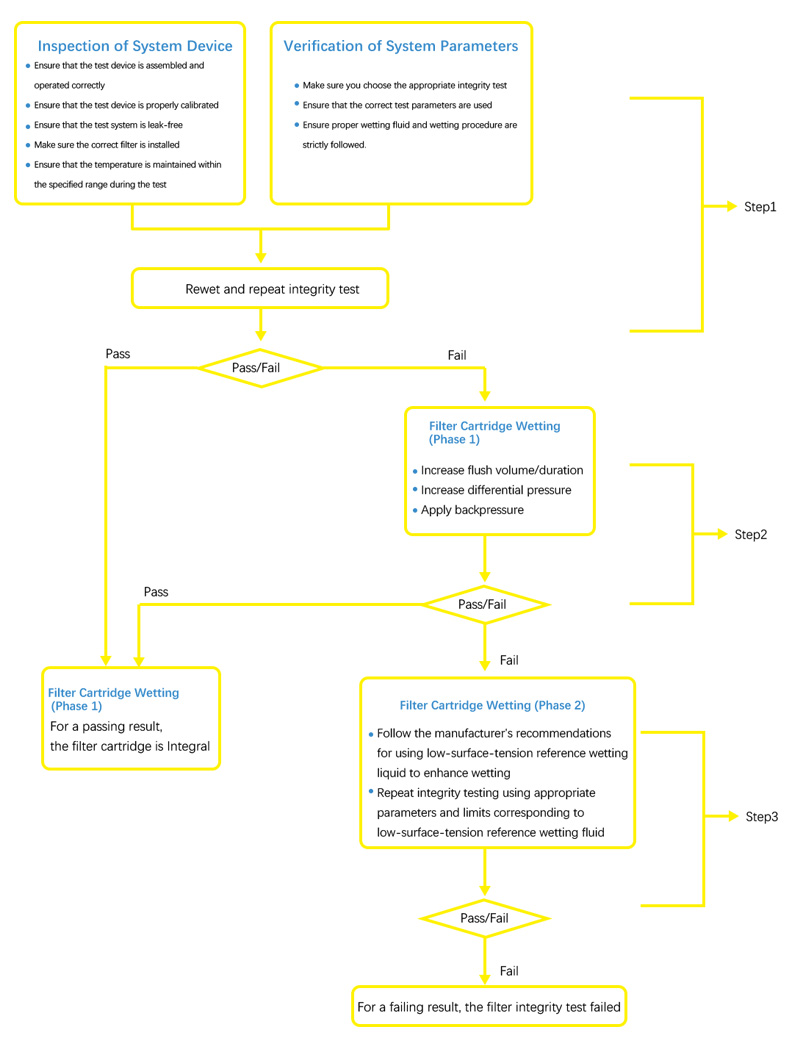
To differentiate between filter damage and other possible causes of "false failure", the following verification steps should be taken:
|
1.Was the appropriate integrity test method selected and the correct test parameters used? |
|
2.Were the correct wetting fluid and wetting procedure used? |
|
3.Is the test system leak-free? |
|
4.Did the temperature of the filter assembly remain stable and within specification during the test? |
When a repeat test is required, the following steps may be used: Rewet the filter cartridge as required by the specification and repeat the test.
If the filter integrity test fails again, the following steps may be used: Apply more aggressive wetting conditions, increase flush volume/time, increase differential pressure and/or apply back pressure.
If the filter integrity test fails again, the following steps may be used:
- Perform integrity test using a low surface tension reference fluid to confirm that changes in cartridge wettability are not related to filter cartridge integrity.
- If the filter fails the test using the reference fluid, the filter fails the test.
If the filter passes the integrity test at any point in the above failure analysis, the filter can be considered intact.
Integrity Test Failure Analysis Tree
Reprinted : Aliothbio Public Account
Latest News
Read more
- Industry Application
- Life Sciences
- water treatment
- Industrial Filtration
- Food & Beverage
- Microelectronics
- Laboratory
- New energy battery
- Contact Us
- [email protected]
- +86-571-87022016
- +86-571-87293027
- +8613675899519
- Subscribe for Join Us!
- Join us and get detail information,technical parameter and new products etc.
CopyRight © Hangzhou Eternalwater Filtration Equipment Co., Ltd. 2002-2025
- [email protected]
- Jenny wu
- +8613675899519
- +86(571) 87022016

 EN
EN  ES
ES AR
AR JP
JP CN
CN