
Product Categories
- Microelectronics
- CMP process
- semiconductor wet etching process
- semiconductor ultrapure water
- electronic chemicals
- process gas filtration
- Food & Beverage
- wine filter
- bottled water filter
- soft drink filter
- beer filtration
- dairy products filtration
- juice filtration
- fruit wine filtration
water treatment
related products
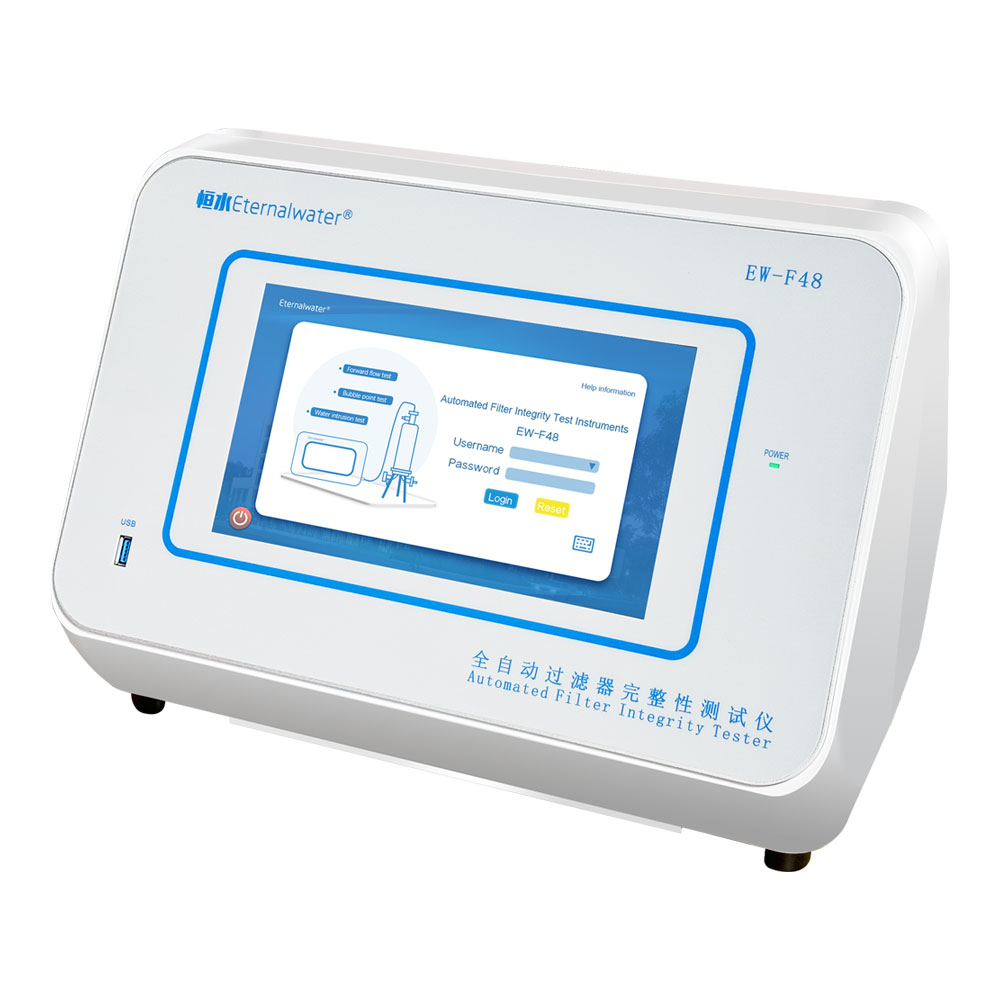
- EW-F48 Series Automated Filter Integrity Tester
- The EW-F48 automated filter integrity tester is a microcomputerized, intelligent, and high-sensitivity precision analysis instrument independently developed by Hangzhou Eternalwater Filtration Equipment Co., Ltd. It is specially used to test the integrity of filter cartridges or membranes in filtration systems. The instrument enables a variety of standard functions, including forward flow test, bubble point test, water intrusion test, combined test of forward flow and bubble point , etc. At the same time of testing, the instrument can automatically perform self-test, automatically control the stabilization time and test time, store and print the current test results, etc.; historical data is displayed graphically to reflect changes in test time and gas flow rate more intuitively.
- EW-F48 Series Automated Filter Integrity Tester.pdf INQUIRY NOW

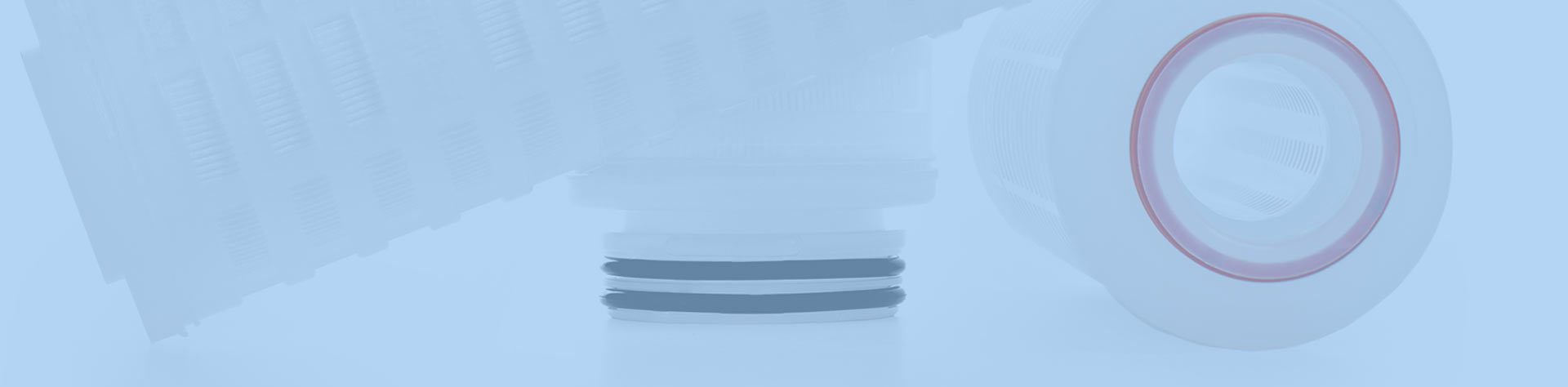
- Bag filter HDL series
- HDL series stainless steel bag filter is made of SUS316L or SUS304 stainless steel. O-shaped sealing design and properly configured sealing ring links ensure reliable system sealing , whether it is a single-bag or multi-bag filter . The built-in filter basket prevents the filter bag from sinking under working pressure and ensures no spillage. It can be used for coarse filtration, medium filtration or fine filtration. It is widely used in industrial water, pharmaceutical water, food and beverage industry, electronics industry, etc.
- HDL series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Security filter HRM series
- HRM series precision filters, also known as security filters, are made of SUS316L or SUS304 stainless steel. Using a single or multiple melt-blown filter cartridges as filter elements, the raw liquid passes through the filter material under pressure, which can effectively remove impurities, sediments and suspended solids in the water. It is usually used in some occasions with large flow rate and is an ideal equipment for pre-filtration.
- HRM series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

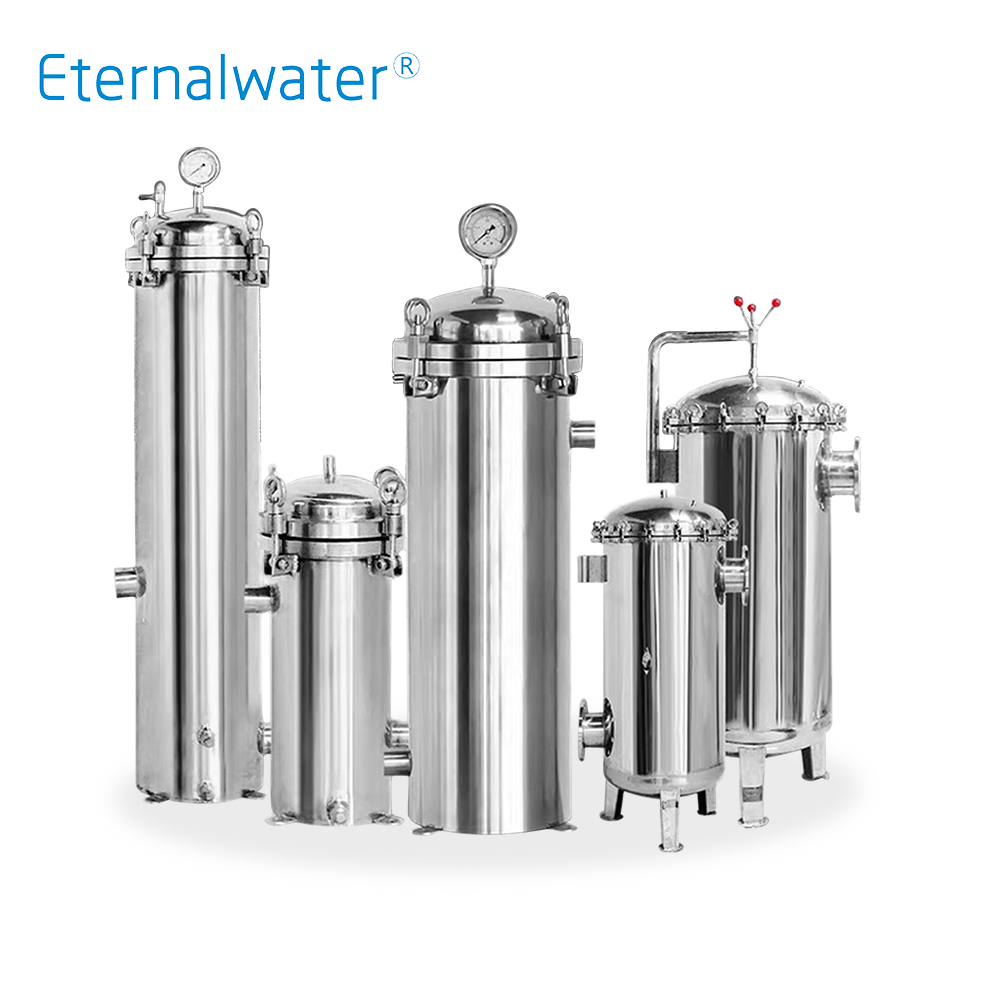
- Large flow filter housing HJM series
- HJM series stainless steel filter housings are made of SUS316L or SUS304 stainless steel. Using single or multiple filter cartridges as filter elements, it has the advantages of high filtration precision, fast filtration speed, no leakage, acid and alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, and easy cleaning. In order to prevent the suspended particles that were not completely removed or newly generated during the pretreatment from entering the reverse osmosis system and protect the high-pressure pump and reverse osmosis membrane, it is usually used in some occasions with large flow rates, especially in the field of water treatment.
- HJM series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Liquid filter bag ELD series
- ELD series liquid filter bags are made of high-quality polypropylene, polyester, nylon, etc. as filter materials and are produced according to specific working conditions and application requirements. The surface can be singed, calendered or coated to effectively prevent fibers from falling off and contaminating the filtrate . The fluffy and uniform three-dimensional filter layer has extremely high capturing power for solid and colloidal particles. The high-strength long fibers make the filter bag have stable filtration efficiency and longer service life. It has the characteristics of high interception rate, strong dirt holding capacity, large flow rate and high pressure resistance. Widely used in liquid impurity removal and filtration in various industries.
- ELD series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- External pressure melt-blown (PP cotton) filter cartridge ERP Series
- ERP series melt-blown filter cartridges are made of hot-melt entangled pure polypropylene microfibers without using any chemical adhesives. The fibers are randomly bonded in space to form a three-dimensional microporous structure, which integrates surface, depth and fine filtration. The deep filtration structure with gradient pores that are sparse on the outside and dense on the inside has strong dirt-holding capacity. According to different production processes, it can be divided into six appearances: smooth/needle- punched/ rough type/orange peel/fine lines/grooved . It can be selected according to actual usage. Mainly It is used in particle interception, clarification filtration, and security filtration. It has good permeability and is a relatively economical pre-filtration filter cartridge.
- ERP Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

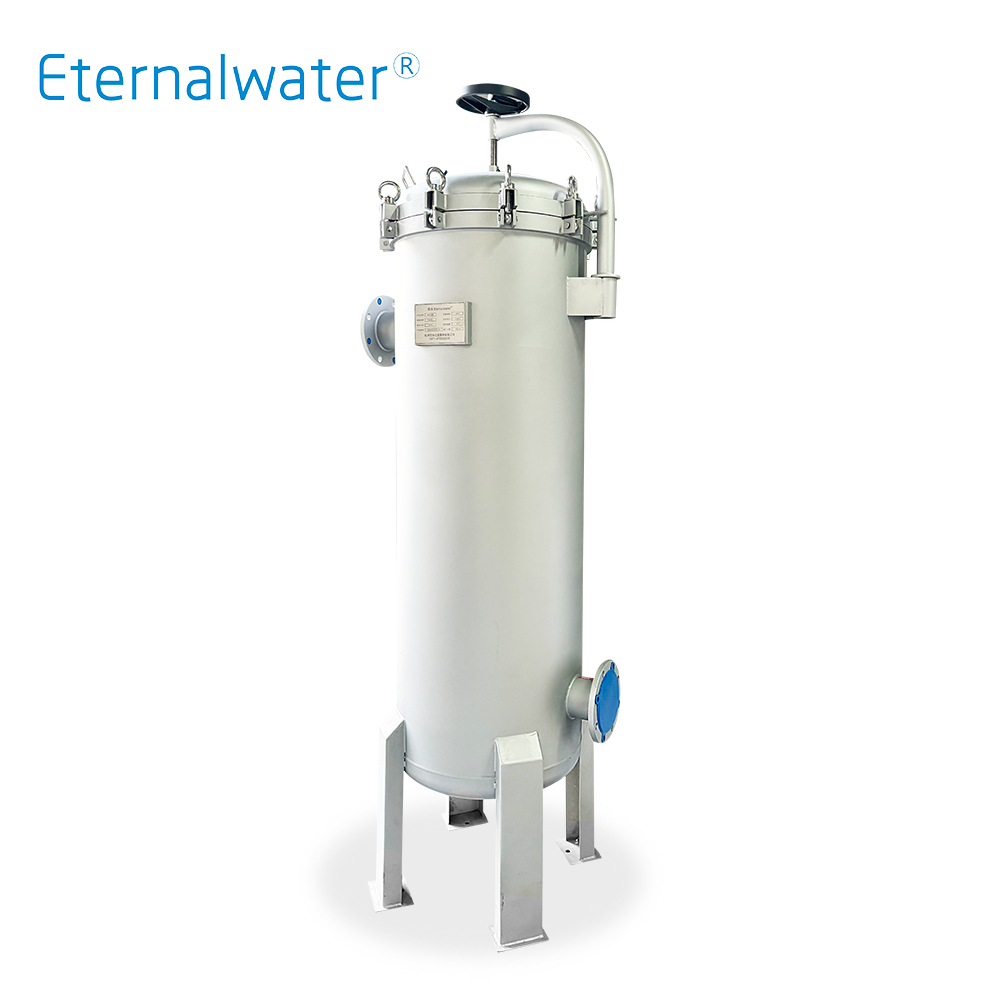
- Bag type large flow filter element END Series
- END series bag-type high-flow filter Cartridges are innovations and breakthroughs in the design and production of traditional bag filters. It can be directly installed in the filters of No. 1 and No. 2 filter bags without further modification to save investment costs. The pleated structure has a larger filtering area and dirt holding capacity, which prolongs the service life and reduces the number of times the filter needs to be replaced. It is easy to install and operate.
- END Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
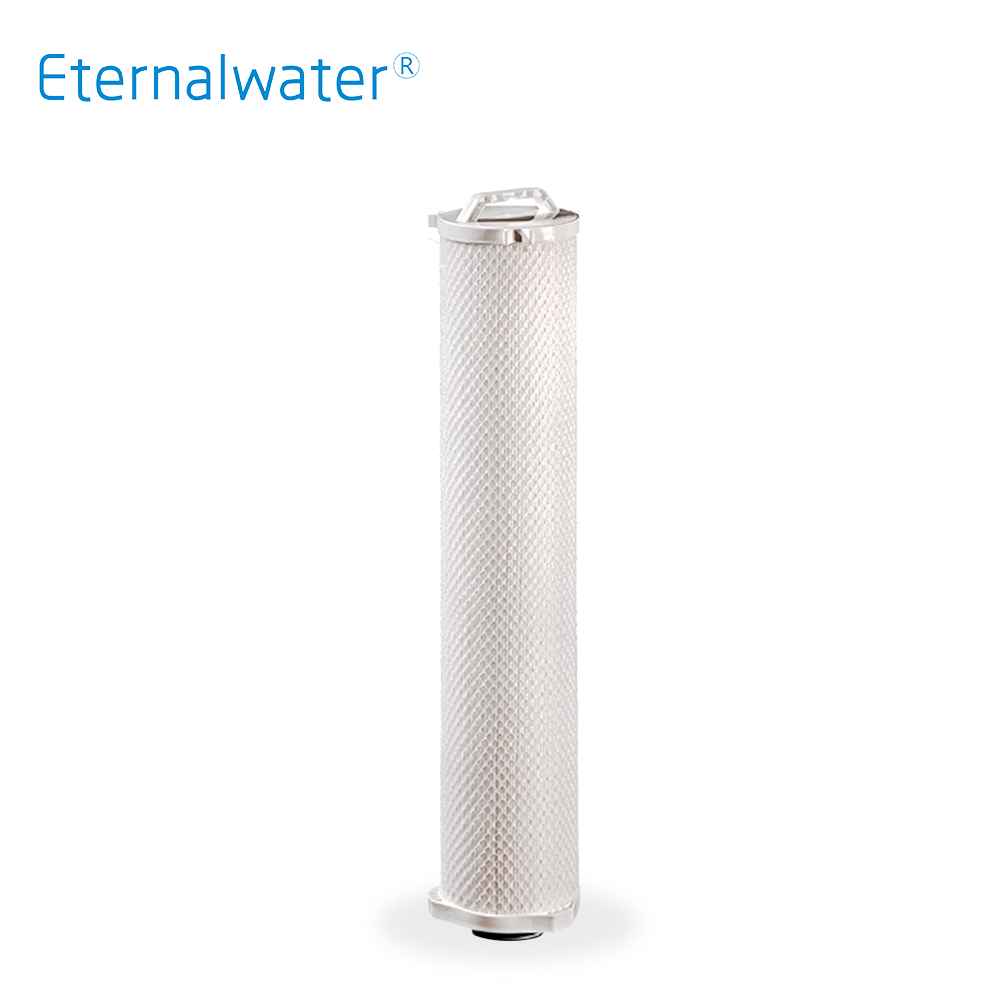

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge EYD Series
- The EYD series has a large flow rate of up to 6.7 inches and a large diameter structure with a high-strength polypropylene support frame inside, and a polypropylene mesh or PP frame for external support. The effective filtration area is greatly increased, the dirt holding capacity can be increased, the number of filter cartridges and the size of the shell can be reduced, and the input cost can be saved.
- EYD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge EWD Series
- EWD series high-flow filter cartridges are designed with double O-rings to ensure the reliability of the seal. The inner frame is made of glass fiber reinforced polypropylene material and wrapped with polypropylene woven mesh. The deep filter structure can effectively intercept impurity particles of different sizes. Strong compression resistance , good chemical compatibility , wide application fields.
- EWD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge EFD Series
- The inner frame of EFD series PHOSPHOR style large flow filter cartridge is made of glass fiber reinforced polypropylene material, wrapped with nylon plastic woven mesh. The deep filter structure can effectively intercept impurity particles of different sizes. Strong compression resistance , good chemical compatibility , wide application fields.
- EFD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- External pressure large flow filter cartridge EBMD Series
- EBMD series 226 connector high-flow filter cartridge adopts deep layer fine polypropylene fiber membrane as the core filter material of the filter cartridge. The large diameter provides a larger filtration area, the internal design center rod strengthens the support, the cross handle design is convenient for installation and removal, and the flow direction is from outside to inside. Can replace imported models: HF40PP005, HF40PP040, HF40PP010, HF40PP070, HF40PP100
- EBMD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
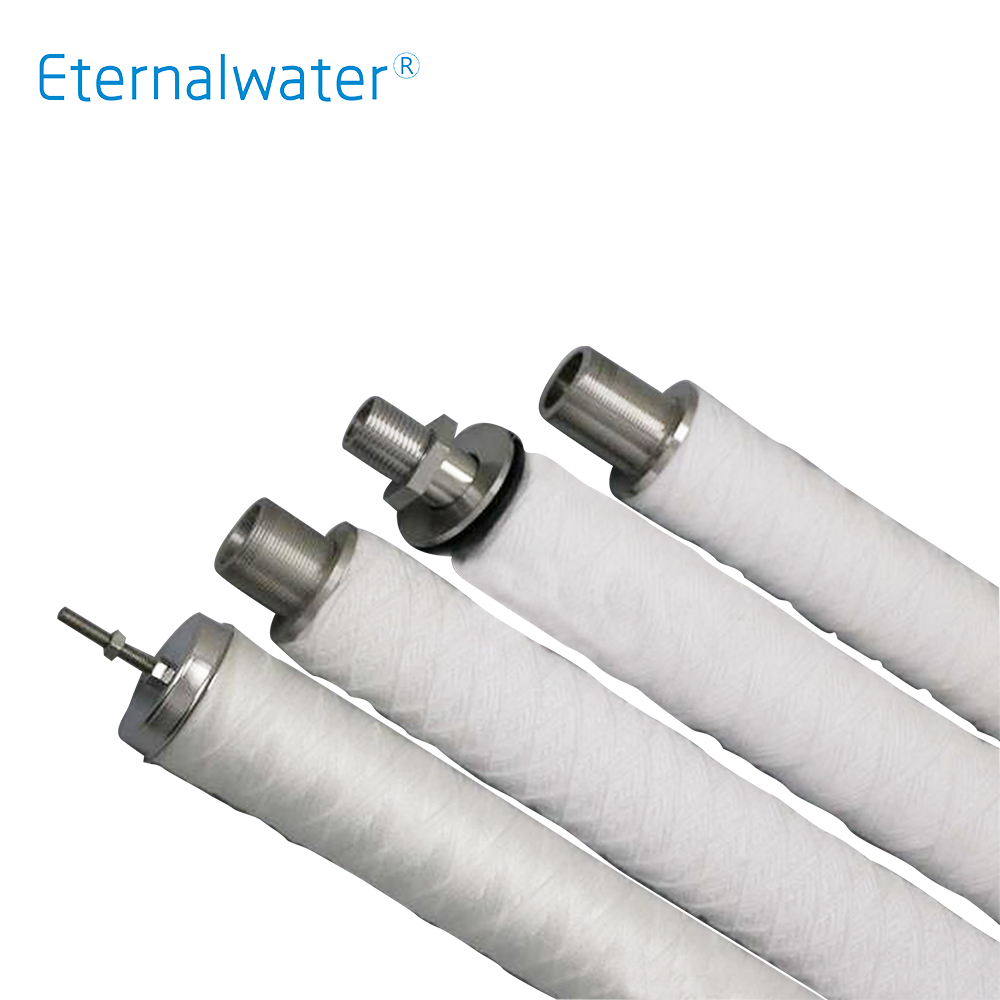

- Backwashable string wound filter cartridges E70D-L Series
- E70D-L series string wound filter cartridges are generally used in the condensate polishing system of power plants. The condensate polishing powder resin covered filter requires stable operation at a relatively high temperature. Its high strength can fully withstand the instantaneous high-pressure impact generated during resin bursting and backwashing. The filter cartridge is controlled by computer, and it is made by winding PP cotton thread or absorbent cotton thread precisely on 304 stainless steel porous skeleton. Ensure that the filter cartridge does not deform, avoid fiber shedding, and ensure the safe operation of the system.
- E70D-L Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
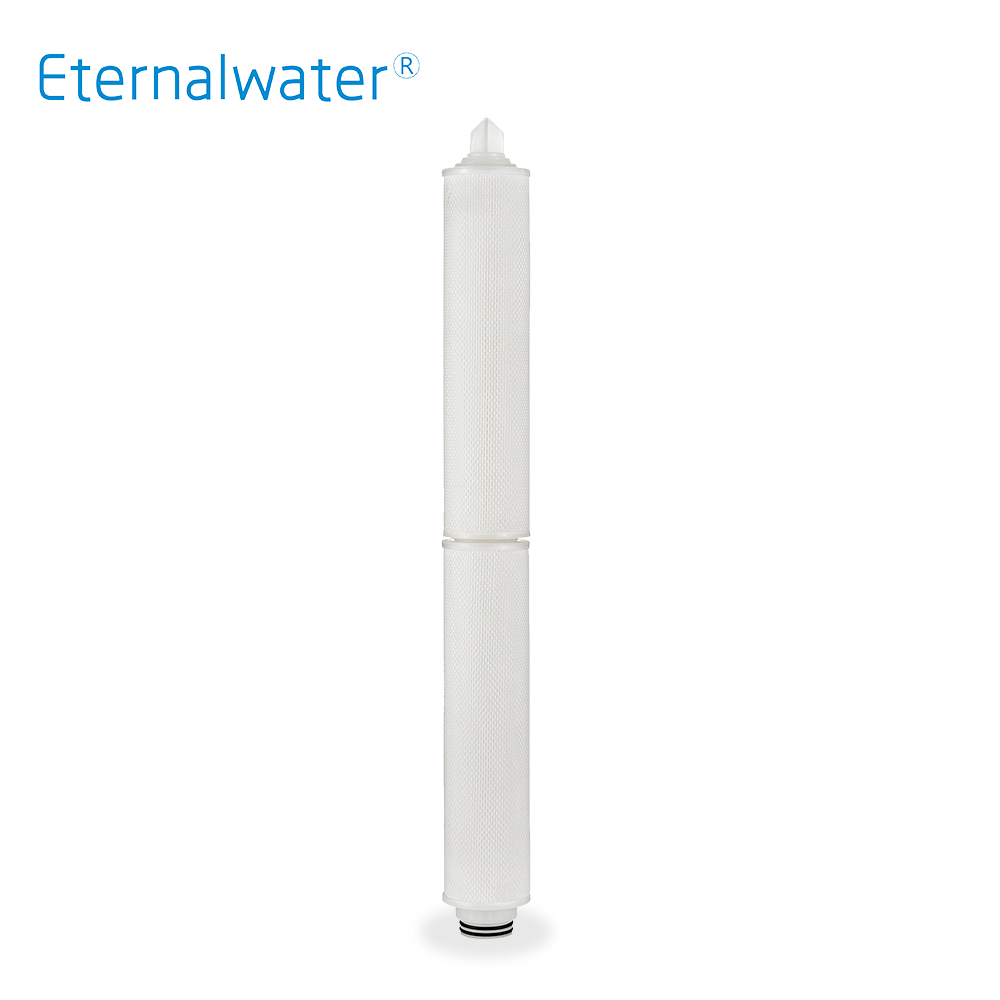

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge E100D Series
- E100D series high-flow filter cartridge adopts a diameter of 100mm and high 226 end cap , which is suitable for medium-flow filtration occasions . The external protection of the filter cartridge adopts PP polypropylene rhombic mesh to protect the filter material from deformation .
- E100D Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge EHMD Series
- The EHMD series high flow filter cartridge adopts the horizontal folding design to maximize the effective filtering surface of the filter cartridge. High-performance polypropylene fiber membrane is used as the filter material, which optimizes its filtration performance to ensure its high-efficiency interception.
- EPD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Tank breathers HV Series
- Breathing filter, installed on all kinds of storage tanks, pure water tanks, sterile and dry ventilation holes. Ensure that the gas is isolated from the outside world through the respirator, and the discharge is smooth. Prevent the storage tank from being polluted by bacteria and dust in the air when the tank is ventilated due to liquid level changes.
- HV Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Sanitary grade pipe filter HG Series
- In-line pipeline filter, the cylinder body is made of high-quality 304 or 316L stainless steel, which has good corrosion resistance, and the design and manufacture meet the requirements of sanitary and GMP. Input on top and output on the bottom, quick opening connection, equipped with exhaust and drain ports, can be used for filtration of gas and liquid.
- HG Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Stainless steel gas filter HQ Series
- The stainless steel gas filter is specially designed and manufactured for gas filtration. It can be used in sterile gas and fermentation gas filtration with PTFE gas sterilization filter cartridge or glass fiber filter cartridge. The filter cartridge is lined with stainless steel, which can withstand high temperature gas filtration, high accuracy, high flow to ensure filtration efficiency and cost of use.
- HQ Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
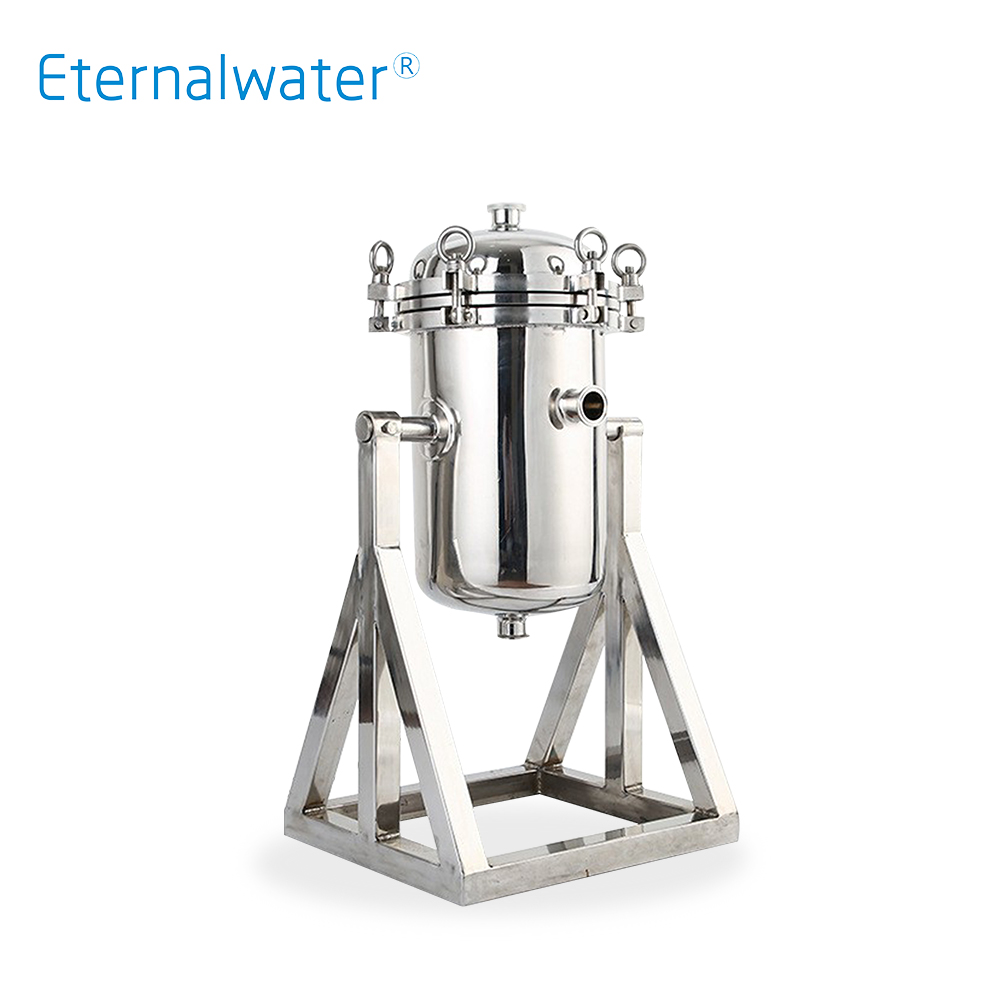

- Flip-over titanium rod filter HTB Series
- The housing of the titanium rod filter is made of 304 or 316L stainless steel, and the titanium metal or stainless steel filter cartridge is used as the filter element, which can achieve a good solid-liquid separation effect by filtering the liquid with high solid content. It has the advantages of high temperature resistance, strong acid, strong alkali, corrosion resistance, and the filter cartridge can be regenerated repeatedly. It is widely used in decarbonization filtration in large infusion and injection production lines.
- HTB Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
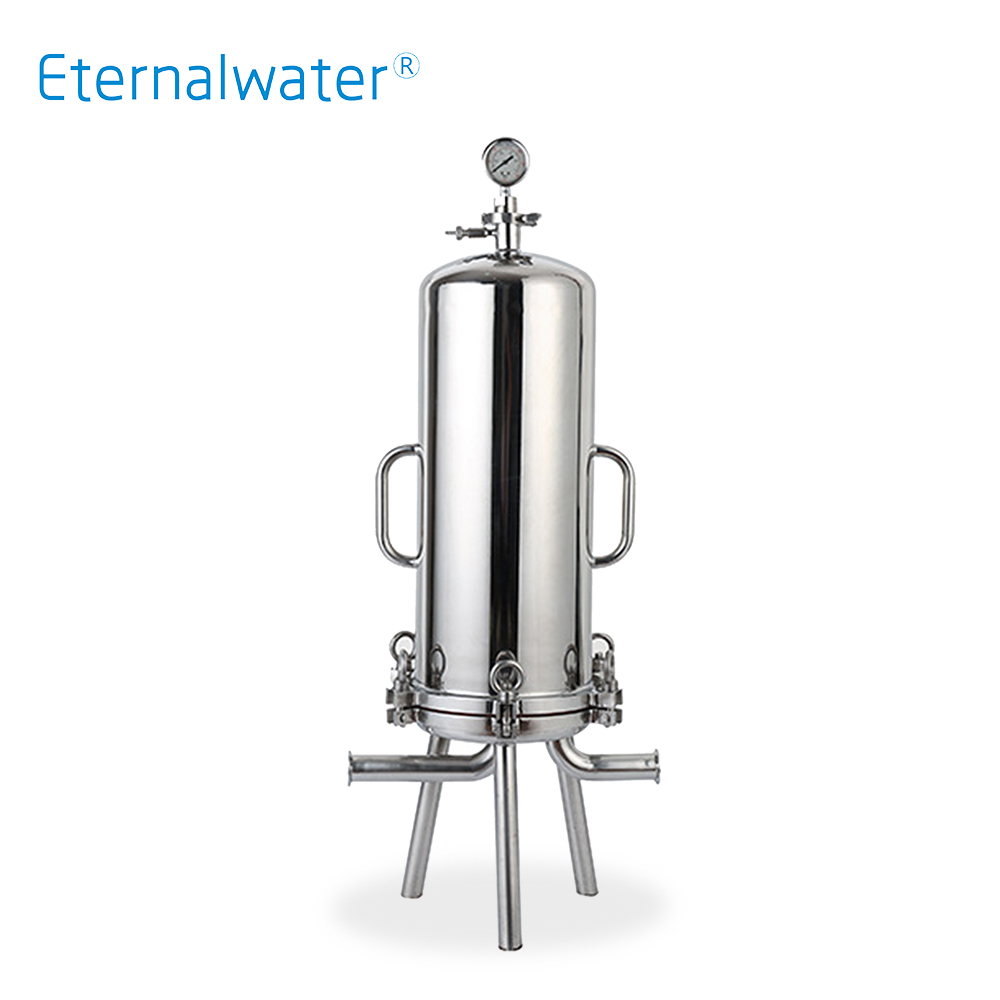

- Multi-core sanitary liquid filter HYD Series
- Cylinder, head, flange, connecting pipe, welding rod and other materials are strictly selected and processed finely. It can be designed according to the requirements of the flow rate and meets the requirements of sanitation and GMP. mechanicalpolished, no sanitary dead corners, easy to clean, no residue.Easy disassembly and installation, scientific structure and many types. Widely used in biopharmaceutical, food and beverage industries.
- HYD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Single core sanitary liquid filter HY1 Series
- Single core stainless steel liquid filter, made of SUS316L stainless steel. One filter cartridge is used as the filter cartridge, and the design meets the requirements of sanitation and GMP. Mechanical polishing, no sanitary dead corners, small flow resistance, acid and alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, convenient cleaning and disinfection, etc. It is suitable for the filtration of small flow in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
- HY1 Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
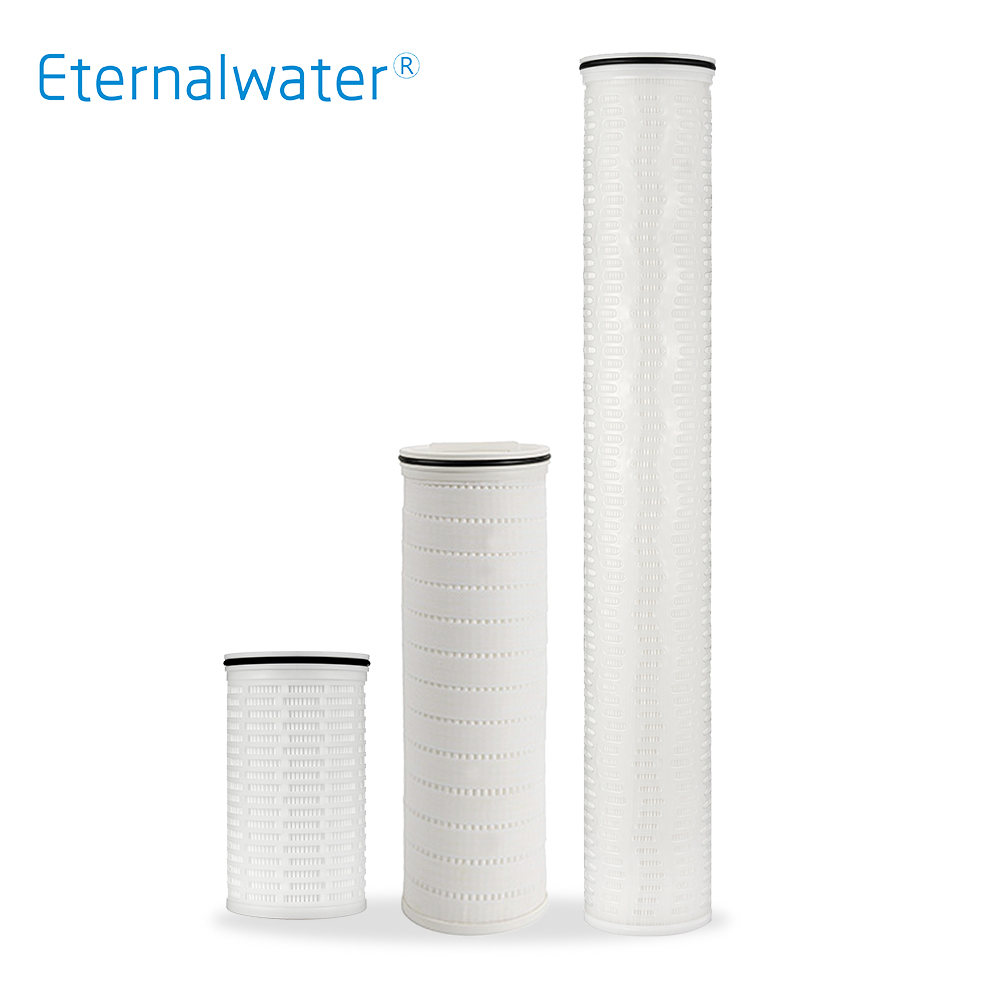

- Internal pressure large flow filter cartridge EPD Series
- EPD series high-flow filter cartridge adopts 6" large diameter structure with one-way opening. The liquid flows from the inside to the outside to ensure that the particles are intercepted inside the filter cartridge. It is made of high-purity polypropylene filter material and support layer by hot-melt welding. Without any adhesive and other additives, with extremely low levels of extractables. Wide chemical compatibility is suitable for filtration needs in various fields.
- EPD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
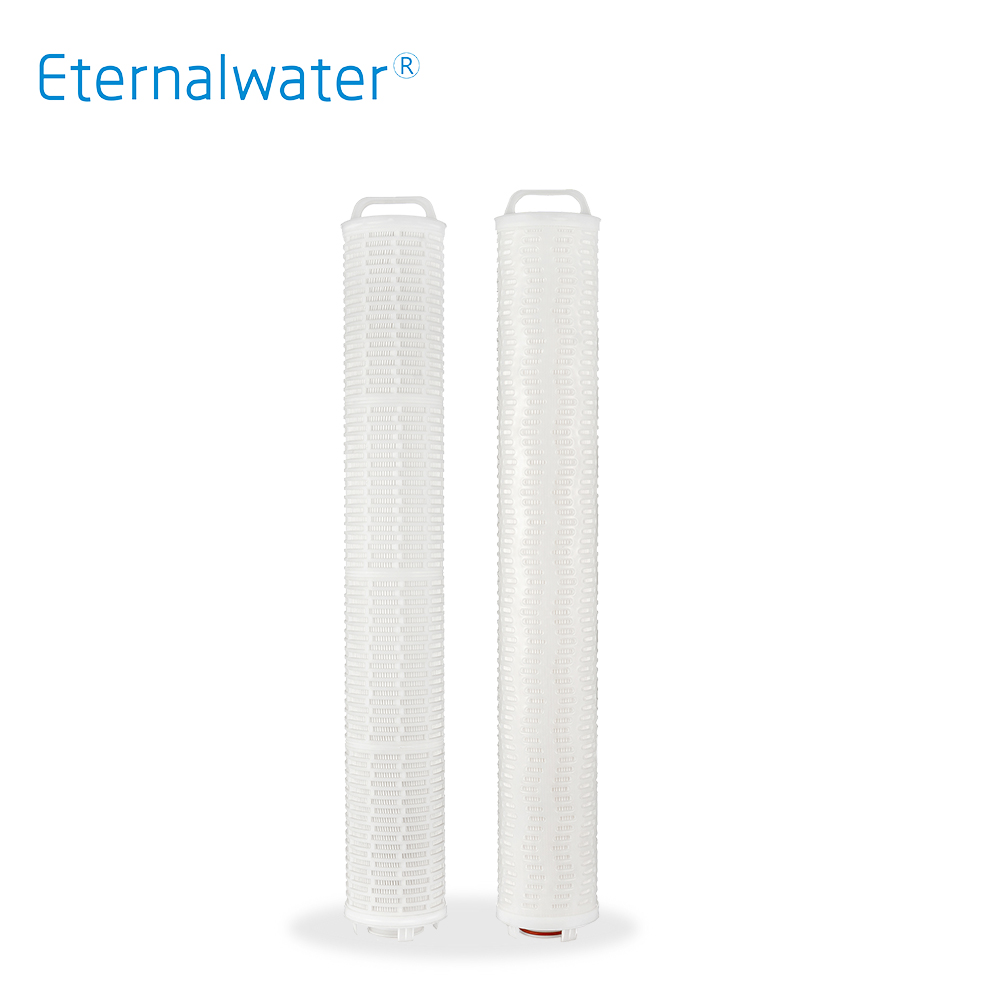

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge EMD Series
- EMD series high-flow filter cartridge adopts high-performance polypropylene membrane/glass fiber membrane, and the pleated design makes the filter cartridge have a larger effective filtration area. Ergonomically designed end handles ensure quick and easy installation and removal. The twist-to-lock design provides a reliable mechanical seal.
- EPD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
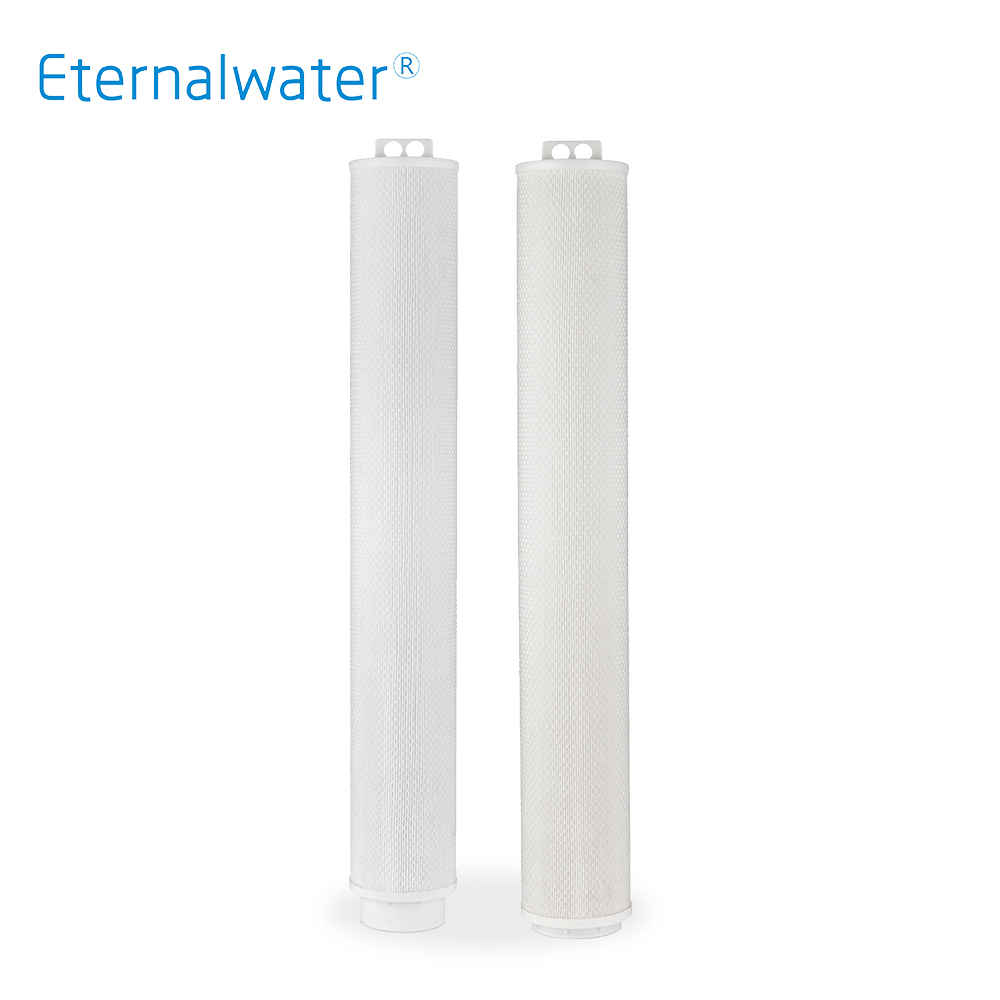

- Outside pressure large flow filter cartridge EKD Series
- EKD series high-flow filter cartridge adopts large diameter (6 " ) structure, folded and welded. It has a high-strength polypropylene support frame inside, and the liquid flow direction is from the outside to the inside. The external support is an integral polypropylene frame and Polyester filter. Two kinds of structures.Special structure makes it have a larger filtration area .
- EKD Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW

- Folded filter cartridge can be backwashed E70D Series
- E70D series pleated filter cartridges are widely used in the pre-filtration of condensate polishing treatment in power plants. High-purity polypropylene filter material is selected, and the whole is hot-melt welded. The internal and external skeleton structure can be reused after backwashing. 10μm filter cartridges are recommended when the unit is started, and 1μm and 4μm filter cartridges are recommended for normal operation.
- E70D Series.pdf INQUIRY NOW
high flow filter cartridge large flow filter cartridge membrane pleated filter cartridge pleated filter cartridge factory capsule filter 0.2 micron capsule filter suppliers capsule filter medical
Read more
- Industry Application
- Life Sciences
- water treatment
- Industrial Filtration
- Food & Beverage
- Microelectronics
- Laboratory
- New energy battery
- Contact Us
- [email protected]
- +86-571-87022016
- +86-571-87293027
- +8613675899519
- Subscribe for Join Us!
- Join us and get detail information,technical parameter and new products etc.
CopyRight © Hangzhou Eternalwater Filtration Equipment Co., Ltd. 2002-2025
- [email protected]
- Jenny wu
- +8613675899519
- +86(571) 87022016

 EN
EN  ES
ES AR
AR JP
JP CN
CN