Definition of Redundant Filtration
2025-07-16 Eternalwater Redundant Filtration is a design strategy used in aseptic processing to significantly reduce the risk of sterilization filtration failure. Its core definition and key elements are as follows:1.Core Definition:
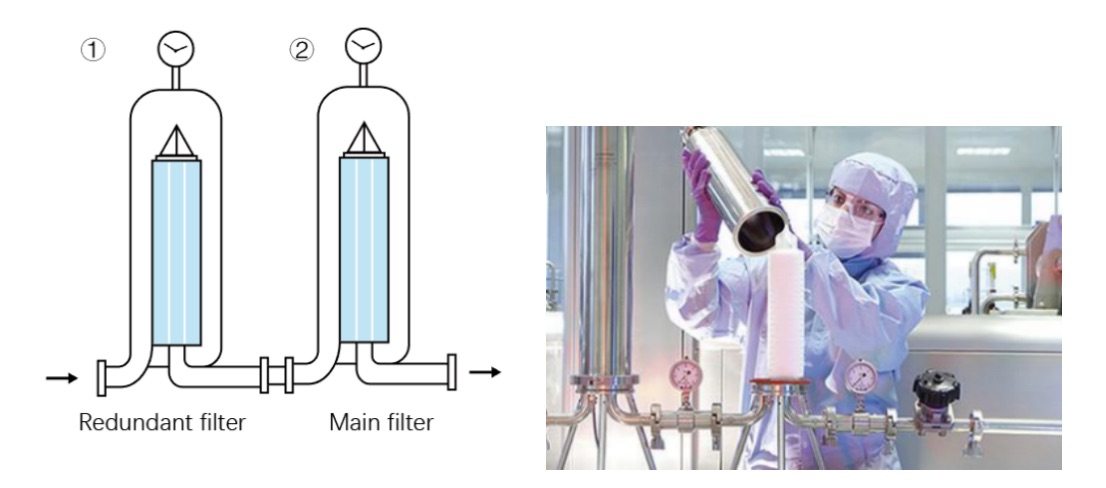
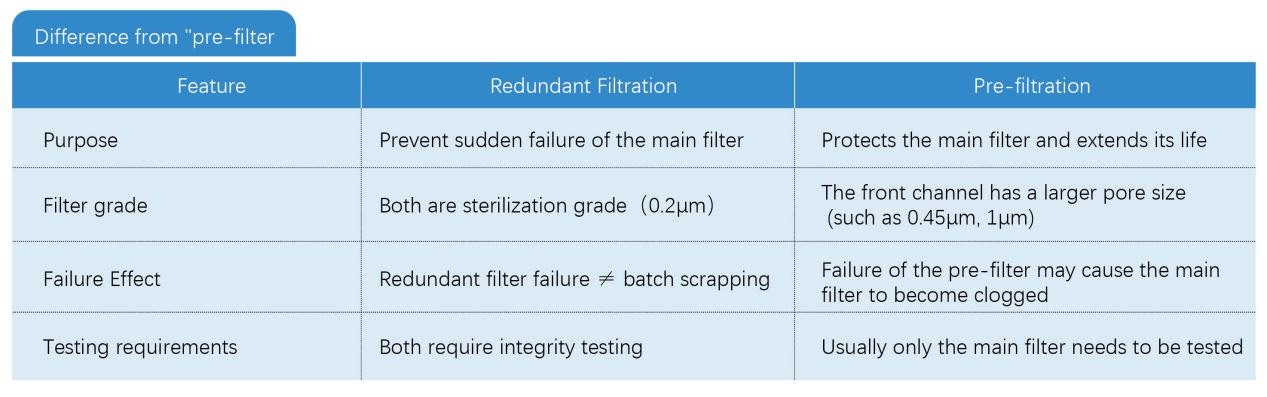
Redundant filtration refers to the use of two sterilizing-grade filters of the same specification (usually 0.22μm or 0.2μm pore size) installed in series, where the first filter is clearly designated as the "redundant filter" and the second filter is designated as the "main filter". The function of the redundant filter is to intercept contaminants as a backup barrier to prevent contamination of sterile products when the main filter fails suddenly during the filtration process (such as membrane damage, seal leakage).
2.Analysis of key elements
①Double physical barrier
The system contains two independent sterilizing grade filters, forming a double protection in series:
● Redundant filter (first stage): provides backup protection for the main filter
● Main filter (second stage): directly ensures the sterility of the final product and is the final barrier
②Design Purpose
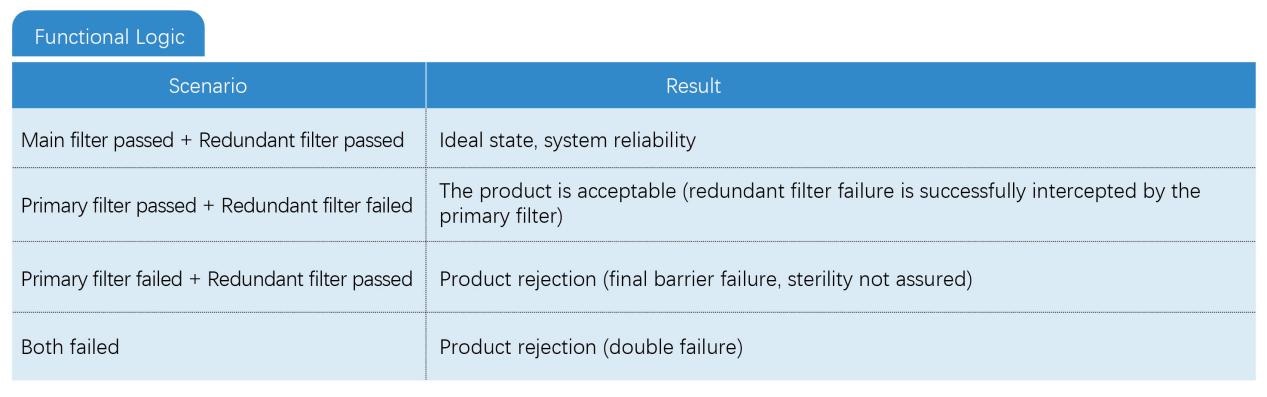
● Dealing with sudden failures: Unpredictable instantaneous failures that may occur in the main filter during the filtration process (such as membrane rupture caused by vibration, accidental loosening of the installation seal)
● Does not replace routine verification: Redundant design cannot prevent systemic risks such as incorrect filter selection, process parameter exceeding the limit, product compatibility issues, etc.
3.Core Requirements
● Same level specifications: The redundant filter and the main filter must both be sterilizing grade (LRV ≥ 7) and have the same material, pore size and size
● Independent integrity test: The two filters need to be tested for integrity (such as bubble point test) after filtration to confirm their respective status
● No “double insurance” logic: Redundant filters are not used to share the filtration load or extend service life, but are designed to provide an “emergency response” for failure of the main filter.
4.
● Final product filtration of sterile preparations (injections, ophthalmic solutions).
● Transfer of biological product bulk solution to sterile preparation system
● Sterile filtration of high-risk culture media or buffers
● FDA Sterile Processing Guide: Clearly requires that critical sterilization filtration should adopt redundant design or subsequent sterility testing
● “For terminally sterilized products, sterilizing filtration should use dual filters or subsequent sterility testing; for aseptically processed products, redundant filtration systems must be used.”
● Detailed definition of verification and operation specifications for redundant filtration
Summary
The essence of redundant filtering: it is an "emergency plan" for the extremely low probability and high risk event of "instantaneous failure of the main filter", which reduces the risk to an acceptable level by adding a physical backup layer, rather than a tool to improve daily filtering efficiency. Understanding this definition can clearly distinguish its fundamental difference from strategies such as series filtering and pre-filtration.
Latest News
Read more
- Industry Application
- Life Sciences
- water treatment
- Industrial Filtration
- Food & Beverage
- Microelectronics
- Laboratory
- New energy battery
- Contact Us
- [email protected]
- +86-571-87022016
- +86-571-87293027
- +8613675899519
- Subscribe for Join Us!
- Join us and get detail information,technical parameter and new products etc.
CopyRight © Hangzhou Eternalwater Filtration Equipment Co., Ltd. 2002-2025
- [email protected]
- Jenny wu
- +8613675899519
- +86(571) 87022016

 EN
EN  ES
ES AR
AR JP
JP CN
CN